Materiality enables us to identify, prioritise, track and report the most important sustainability issues. To identify the top 20 environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues, we conducted an extensive stakeholder engagement exercise in FY 2018-19. These issues were rated as ‘high priority’ by stakeholders, in addition to being key to business success in the short, medium and long term. The material economic issues were revisited through various stakeholder engagement processes and business reviews by the senior leadership.
Tata Steel’s strategy and planning process incorporates the material issues by mapping them to its long-term Strategic Objectives (SOs). These issues are reviewed periodically by the respective owners and by the senior management.


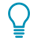



| Material issues | Measures | Linked key performance indicators (KPI) |
|---|---|---|
|
Business growth |
Focus on organic and inorganic growth Scaling of adjacent businesses Entering into new market segments |
Crude steel production capacity Revenue from the New Material Business, Service & Solutions, Commercial Mining Business Revenue from High End and Downstream products and solutions |
|
Long-term profitability |
Attain and retain leadership in chosen segments Raw material security Enhance operational efficiency Shikhar25 cost management initiatives |
Market share in chosen segments Captive coal (%) and captive iron ore (%) EBITDA Savings through Shihkar25 initiatives |
|
Product and service quality |
Product and process innovation Value engineering and customer service teams Innovative routes to market |
Number of new products and services Customer satisfaction index Quality complaints Revenue from sales on digital platforms |


| Material issues | Measures | Linked KPIs |
|---|---|---|
|
CO2 emission |
5 Tonne Per Day (TPD) carbon capture pilot plant commissioned at TSJ – captured CO2 being utilised for water treatment at a steelmaking unit Collaboration with SHELL and Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) to explore decarbonisation technologies |
GHG emission intensity Total GHG emissions for steel making sites |
|
Air pollution |
Upgradation of existing air pollution control equipment and installation of state-of-the-art dust control technology |
Dust emission intensity |
|
Water consumption and effluent discharge |
Minimising freshwater consumption by upgradation of existing water treatment and cooling tower systems to increase efficiency Reusing treated waste water from sewage and effluents for industrial purpose |
Specific freshwater consumption Effluent discharge intensity |
|
Energy efficiency |
Process optimisation initiatives such as waste heat recovery systems, top recovery turbine by-product gas utilisation |
Energy intensity |
|
Renewable and clean energy |
Feasibility analysis for solar projects completed and projects initiated |
Renewable purchase obligation Power generated through renewable sources |
|
Waste management |
Enhance steel scrap usage in steelmaking 100% solid waste utilisation Enhance value from by-products |
Steel scrap supplies to LD shops LD slag utilisation Solid waste utilisation Revenue from by-products |
|
Supply chain sustainability |
Identification of critical supply chain partners and engagement with them on Tata Steel Responsible Supply Chain Policy |
Number of partners made aware on Tata Steel Responsible Supply Chain Policy Number of partners assessed on Tata Steel Responsible Supply Chain Policy |
|
Biodiversity |
Biodiversity Management Plans (BMPs) for Jamshedpur and Kalinganagar developed (BMPs developed for 11 locations cumulatively till FY 2020-21) Over 2.98 lakh saplings of native species planted across locations in FY 2020-21 |
Total sites covered under BMPs |
|
Circular economy |
Steel scrap processing unit commissioned at Rohtak, Haryana with a 0.5 MnTPA capacity Advocacy with various government and industry bodies to build scrap utilisation networks |
Capacity of steel recycling business |


| Material issues | Measures | Linked KPIs |
|---|---|---|
|
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) |
Build Safety Leadership capability at all levels to achieve zero harm Improve competency and capability for hazard identification and risk management Achieve zero harm to contract employees by strengthening deployment of Contractor Safety Management Standard Reduction in safety incidents on road and rail to ensure zero fatalities inside plant premises Excellence in Process Safety Management (PSM) Establishment of industrial hygiene and improvement in occupational health |
LTIFR TRIFR LTI Fatalities Health Index |
|
Labour relations |
Concluded wage revision with structural changes Introduction of Connected Workforce Management, POD working system (for COVID-19) and People Care to ensure employee safety |
Performance in Employee Engagement Survey |
|
Drinking water |
Enabling community-led access to safe drinking water for identified households |
Number of water harvesting structures constructed/repaired Number of lives reached |
|
Local sourcing of labour |
Recruiting indigenous (SC/ST) people in the workforce Improving vendors’ share of business from SC/ST communities by training them to match our requirements for various products and services |
Number of local suppliers Business volume of local suppliers % of Affirmative Action (AA) community in the workforce |
|
Talent retention |
Provide flexibility to employees through agile working policy Creating an inclusive workspace to attract and retain diverse talent including Persons with Disabilities (PWDs) and LGBTQ+ community Development of workforce capability through various programmes |
Attrition rate (overall) Percentage of women in workforce Investment in employee training and development |




| Material issues | Measures | Linked KPIs |
|---|---|---|
|
Technology, product and process innovation |
Focus on technology, digital and disruptive innovation overlaid on a culture of continuous improvement Addressing environmental concerns by developing and implementing breakthrough technologies progressively at larger scale Building a sustainable business portfolio, which is resilient against steel business cyclicality |
Number of patents received Number of new products developed Number of start-ups engaged Number of alliances created Number of breakthrough projects |
|
Going beyond compliance and setting trends for future regulations |
Setting up Steel Recycling Business (SRB) for foray into organised scrap play in India Adoption of best available technologies and implementing projects for resource efficiency and reducing carbon footprint Strengthened collaborations with technical institutes, technology start-ups and academia for technology leadership, climate change and other environmental issues Diversity and Inclusion Policies for women in workforce, persons with disabilities (PWDs) and LGBTQ+ community; for example, women in all shifts in mines |
Capacity of SRB Performance on various environmental parameters – air, water, waste Number of collaborations with external partners Workforce diversity indicators - % women/PWDs/LGBTQ+ in workforce |
|
Greater sustainability disclosures |
Consistent improvement in our disclosures through the Engagement with ESG rating agencies for improving disclosure practices and enhance access to sustainable finance Updating Tata Steel website periodically to enhance transparency and meet stakeholder requirements |
Scores and achievements in: ESG ratings |
|
Greater stakeholder engagement |
Enhancement of specialised channels such as public meetings, vendor-focussed committees, 'Speak Up' toll-free number, platforms such as conference and construction conclave, zonal and similar events Setting up special COVID-19 care helplines and medical facilities |
Performance in various surveys
conducted periodically for Stakeholder
categories, including: |
|
Responsible advocacy for the steel and mining sector |
Effective policy formulation to improve the ease and cost of doing business in our areas of operation by ensuring a level playing field and advocating global best practices. |
Advocacy for improving cost of doing business and ease of doing business |
|
Technical knowledge transfer and capacity building for relevant partners |
Collaboration with suppliers through Supplier Relationship Management Programme Conduct Vendor Capacity Advancement Programmes (VCAP) for suppliers Engagement with customers through Early Vendor Involvement (EVI) and Value Analysis and Value Engineering (VAVE) initiatives Awareness sessions for suppliers, Steel Processing Centres (SPCs) and distributors on Ethics, Health and Safety, Responsible Supply Chain Policy and other relevant issues |
Number of VCAP sessions conducted Number of awareness sessions conducted Number of supply chain partners made aware on Responsible Supply Chain Policy Number of EVI and VAVE projects |
Strategic objective
Leadership in India
SO2Consolidate position as global cost leader
Attain leadership position in adjacent businesses
SO4Leadership in sustainability
Capitals
 Financial capital
Financial capital Manufactured capital
Manufactured capital Intellectual capital
Intellectual capital
 Human capital
Human capital Natural capital
Natural capital Social and Relationship capital
Social and Relationship capital