Enterprise Risk Management
The objective of our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is to prepare the Company to become ‘Risk Intelligent’ i.e. to strengthen risk resilience to significant risk exposures, provide agility and a competitive edge with the goal of preserving as well as enhancing long-term value for stakeholders.
The objective of our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is to prepare the Company to become ‘Risk Intelligent’ i.e. to strengthen risk resilience to significant risk exposures, provide agility and a competitive edge with the goal of preserving as well as enhancing long-term value for stakeholders.
the phased rollout of the ERM framework and ensures uniform deployment across the Tata Steel Group. The final ownership for and implementation of risk response strategies rests with the senior executives of the functional units or the risk owners.
Our ERM framework has been developed with inputs based on best practices of leading companies and international standards & references such as COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organisation of Treadway Commission) & ISO 31000. The framework has effectively been used to identify and analyse unforeseen risks, resulting in the management taking risk informed decisions. The ERM team ensures the effectiveness of the process through
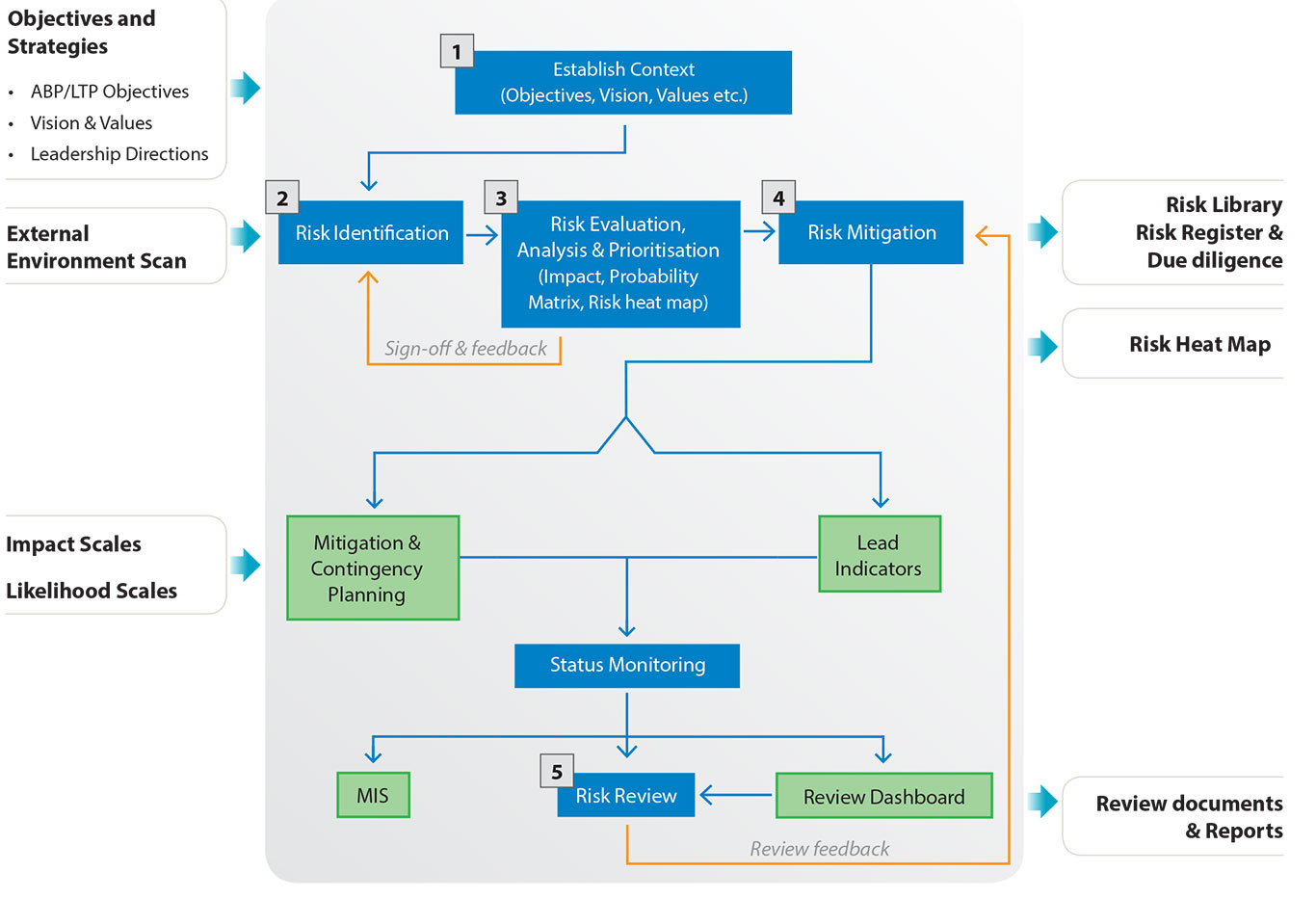
its engagement with a wide spectrum of internal stakeholders via a bottom up five step process depicted in the diagram, with the senior management actively monitoring, reviewing and guiding the process at all stages.
Overview of Key Risks
As a global organisation, we are exposed to risks and opportunities arising out of a dynamic macroeconomic environment that could impact our business objectives, strategies and hamper our ability to create value over the short, medium and longterm. Our key risks, linkage to strategic priorities, impact on various capitals and the mitigation strategies are summarised in the adjacent table.
| Risks | Potential Impact | Impacted Capital | Risk Response Strategies |
| Strategic Risks | |||
| Adverse macro environment coupled with global steel capacity may impact our operating markets and net realisations stressing our cash flows and ratings. | Profitability, Financial, Flexibility | Financial Capital |
|
| Long-term growth of the organisation may be hampered in case of failure of capacity expansion projects, restructuring. | Growth & Expansions | Financial Capital |
|
| Operational Risks | |||
| Failure to maintain adequate health and safety standards may cause us to incur significant costs, liabilities and damage the Company’s reputation. | Human Safety, Employee Morale | Human Capital Social and Relationship Capital |
|
| Absence of social license to operate may cause business disruptions. | Business Continuity | Financial Capital Social and Relationship Capital |
|
| Human resource risks and/or low productivity may challenge the Company’s competitiveness. | Employee Productivity, Cost | Human Capital |
|
| Legal & Compliance Risks | |||
| Absence of raw materials linkage due to adverse regulatory environment and/or its price volatility may threaten Company’s profitability. | Business Continuity, Cost, Volume | Natural Capital Manufactured Capital |
|
| Regulatory and environmental non-compliances may cause the Company to incur liabilities and damage the Company’s reputation. | Regulatory Compliance |
Manufactured
Capital Financial Capital Social and Relationship Capital |
|
| Foreign exchange rate volatility may affect the outcome of commercial transactions. | Profitability | Financial Capital |
|
| Impairment of tangible and intangible assets may affect the Company’s key financial ratios. | Financial Ratios | Financial Capital |
|
Focus Areas
To further strengthen and improve upon the process and framework, the Company will going forward focus on:
1. Widening the reach and depth of engagement across the Company in the planned phased manner.
2. Better integration of ERM with business processes.
3. Automation of the ERM process.
4. Launch of e-learning modules and packages/ manuals / documented procedures for ready referrals.
5. Initiation of external training sessions and programmes to spread awareness.
The India Opportunity
Urbanisation directly influences steel consumption. India is only about 31% urban presently and with higher migration, newer
centres of development and Government programmes such as the Smart City Mission, the rate of urbanisation and urban
renewal is expected to rise significantly in the near-future. India’s per capita steel consumption is very low (at 61kg) compared
with China (at 540kg), pointing to a significant headroom for consumption growth.
Demographic trends further support the case for the increasing steel demand in India. Each year approximately 12 mn people join the workforce in India. There is a corresponding increase in demand for housing, transportation and public infrastructure, all of which are major drivers for steel demand.
Raw material costs form a significant portion of the steel making cost. India has adequate reserves of high quality Iron ore giving steel manufacturers in India a price advantage.
Competitive labour costs in India allow steel producers a distinct advantage. Globally, labour constitutes approximately 8-10% of the total cost of making and selling steel. We seek to leverage this advantageous position and strengthen our status as a low-cost producer of steel.
| Raw Material | Growth | Productivity | Customer, Market and Product segments | Digital Technologies | |
|
|
High quality, low cost iron ore available at close proximity to the manufacturing plant. |
Stable demand growth in India driven by a young demography and trend of urbanisation. Focus of Government on infrastructure development and ‘Make In India’ initiative. |
Employee productivity low as compared to peers. |
Potential for customised products and services. |
Leverage digital technologies to make the Company more agile, enhance productivity and profitability. |
 |
Invest in mining assets for securing iron ore reserves. |
Enhance steel producing capacity
|
Improving work practices and increasing automation. |
Increase revenue from services and solutions and B2C. Enter new segments. |
Seeding initiatives via organisationwide mobilisation, pilots and capability building. |


